Introduction
Heart disease is one of the leading causes of death worldwide, affecting millions of people
each year. Even though it is a serious condition, many types of heart disease can be
prevented or managed with lifestyle changes, early diagnosis, and proper treatment. In this
blog post, we’ll explore everything you need to know about heart disease in simple language,
including its causes, symptoms, types, prevention tips, and available treatments.
This article is your go-to guide and a cornerstone for future deep dives into related heart
health topics.
1. What Is Heart Disease?
Heart disease is also called Cardiac disease. This General term for several problems that affect the heart and blood vessels.
It is also called cardiovascular disease (CVD). This includes conditions like:
- Blocked or narrowed blood vessels (which can lead to heart attacks and strokes)
- Problems with heart rhythm (arrhythmias)
- Issues with the heart muscles or valves.
- Heart disease makes it hard for your heart to pump blood properly, which affects your entire
body.
2. Common Symptoms
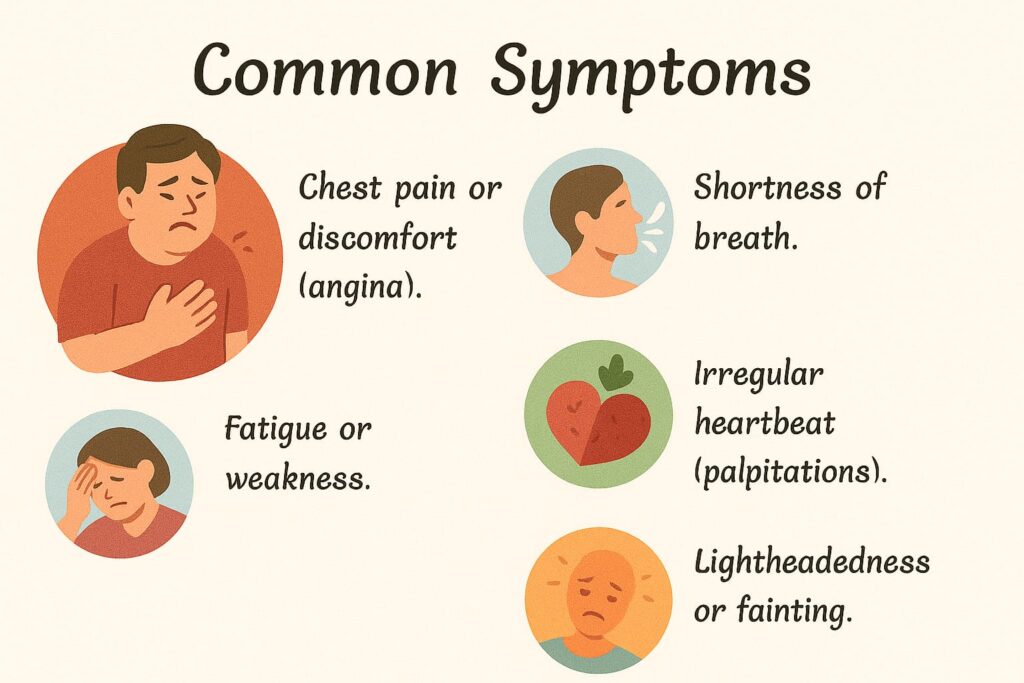
Symptoms can vary depending on the type of cardiac disease, but common signs include:
- Chest pain or discomfort (angina).
- Shortness of breath.
- Fatigue or weakness.
- Irregular heartbeat (palpitations).
- Swelling in the legs, feet, or abdomen.
- Lightheadedness or fainting.
Some people, especially women, may experience unusual symptoms like nausea, back
pain, or jaw pain. To know more about heart disease symptoms.
To read more about symptoms, click here
3. Types of Heart Disease
Here are some of the most common types:
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Caused by plaque buildup in the arteries that supply blood to the heart. - Ischemic Heart Disease
Occurs when reduced blood flow damages the heart muscles. - Rheumatic Heart Disease
A result of untreated strep throat or rheumatic fever is damaged heart valves. - Valvular Heart Disease
Involves malfunctioning heart valves that affect blood flow. - Congenital Heart Disease
Heart structure problems are present at birth.
4. What Causes Heart Disease?

Several risk factors contribute to the development of this disease. These include:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Poor diet
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Stress and mental health issues
5. Prevention: Can You Prevent This?
Yes, it can be prevented or delayed through a healthy lifestyle
changes:
- Eat a heart-healthy diet (fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins)
- Exercise regularly (at least 30 minutes a day)
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol
- Control blood pressure and cholesterol
- Manage stress and mental health
To know about super foods that boost your heart health, CLICK HERE
6. Diagnosis and Tests

If your doctor suspects you have heart disease, they may recommend one or more of the following tests:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): Measures your heart’s electrical activity.
- Echocardiogram: Uses sound waves to create images of your heart.
- Stress Test: Shows how your heart performs under physical stress.
- Cardiac CT or MRI: Provides detailed pictures of your heart and blood vessels.
- Blood Tests: To check cholesterol, triglycerides, and other heart-related markers.
- Angiography: A special X-ray using dye to see blockages in your arteries.
Early diagnosis improves your chances of effective treatment.
7. Treatment Options for Heart Disease
Cardiac disease treatment depends on the type and severity of your condition. It may include one or more of the following:
Lifestyle Changes
The first step is often adopting a healthier diet, increasing physical activity, quitting smoking, and managing stress.
TO KNOW ABOUT PHYSICAL ACTIVITY, CLICK HERE
Medications
Doctors may prescribe:
- Blood pressure medicines
- Cholesterol-lowering drugs
- Blood thinners
- Medications to control the heartbeat or relieve chest pain
Medical Procedures
Some cases may require:
- Angioplasty: A tiny balloon is used to open blocked arteries.
- Stent placement: A small tube is inserted to keep arteries open.
- Bypass surgery: Blood is rerouted around blocked arteries.
- Valve repair or replacement: For damaged heart valves.
- Pacemaker or defibrillator: To correct heartbeat problems.
Ongoing Care
Cardiac disease usually requires long-term monitoring and follow-up with your doctor to adjust treatments and prevent complications.
Final Thoughts
This Disease may be common, but it’s also largely preventable and manageable.
With the right knowledge, early detection, and healthy habits, you can protect your
heart and live a longer, healthier life.
Start today, your heart will thank you.
To read more, click here

